Help
Aging is a natural part of human life. However, recent discoveries indicate that pharmacological approaches used for the improvement and possibly, for the delay of the aging process, might shed a new light on this topic. Traditional anti-aging drugs are directly screened on animal models and difficult to carry out clinical transformation because it is blind that lacks the necessary computational screening process in the early stage. ACDB is a comprehensive anti-aging compounds database, with the aim of providing a large amount of publicly available resources on anti-aging compounds, and to be suitable for artificial intelligence to speed development of anti-aging drugs. This database provides functions such as browsing, searching, viewing and downloading for anti-aging compounds, species, experimental information and reference.
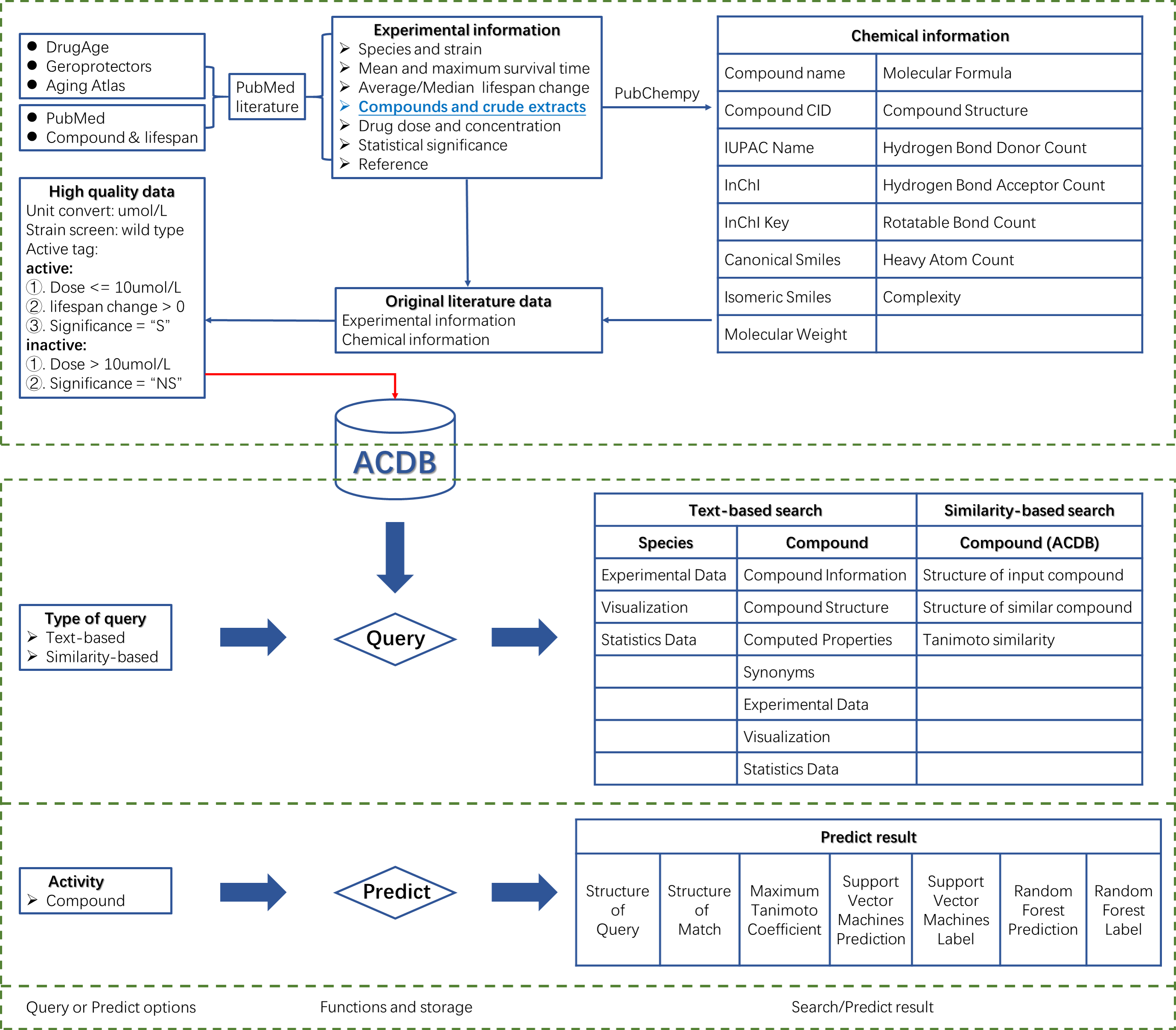
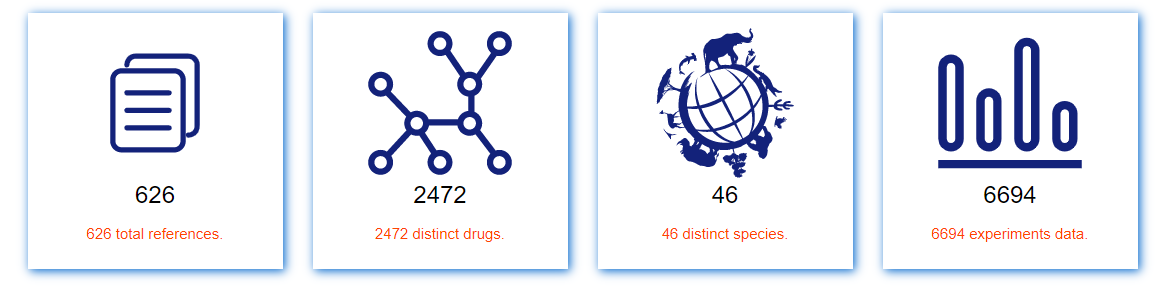
The current version of ACDB documented a total of 6694 experiments data from 626 validated publications, which includes more than 2400 distinct drugs. Furthermore, ACDB covers experiments of nearly 46 species and provides detailed information including original data source, species and strain, compound structure, statistical significance and activity tag, drug dosing and concentration, mean survival time and maximum survival time.
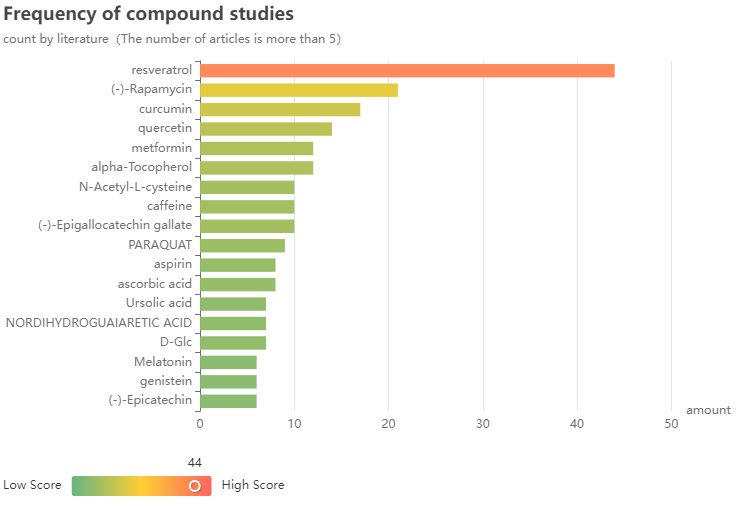
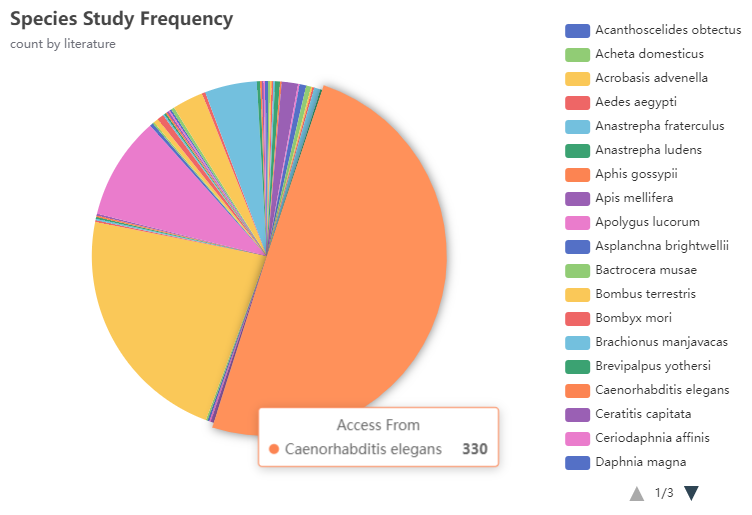
Visual charts show the current drugs and species of hot research in the field of aging. Up to now, 44 articles have investigated resveratrol anti-aging activity and 330 articles have studied the mechanism of aging by using Caenorhabditis elegans as the experimental object.
Users browse the database by clicking 'Browse' button on navigation bar and search specific information at the bottom of each column or the entire database in the upper right corner. Users view species, compound and reference details by clicking hyperlinks. Some uninteresting columns will be hidden by clicking the button in "Show/Hide Columns".

Species search and compound search were provided in search page. Users search species by selecting dropdown menu and search compounds by searching compound name, Smiles, CID, Iupac name, Inchi, Inchikey and Molecular formula. In addition to providing text-based search, ACDB provided similarity-based structure search. Users can convert chemical information and 2D chemical structure of compound by using KingDraw in similarity-based structure search section. Similarity-based structure search can also be mapped into the PubChem database.
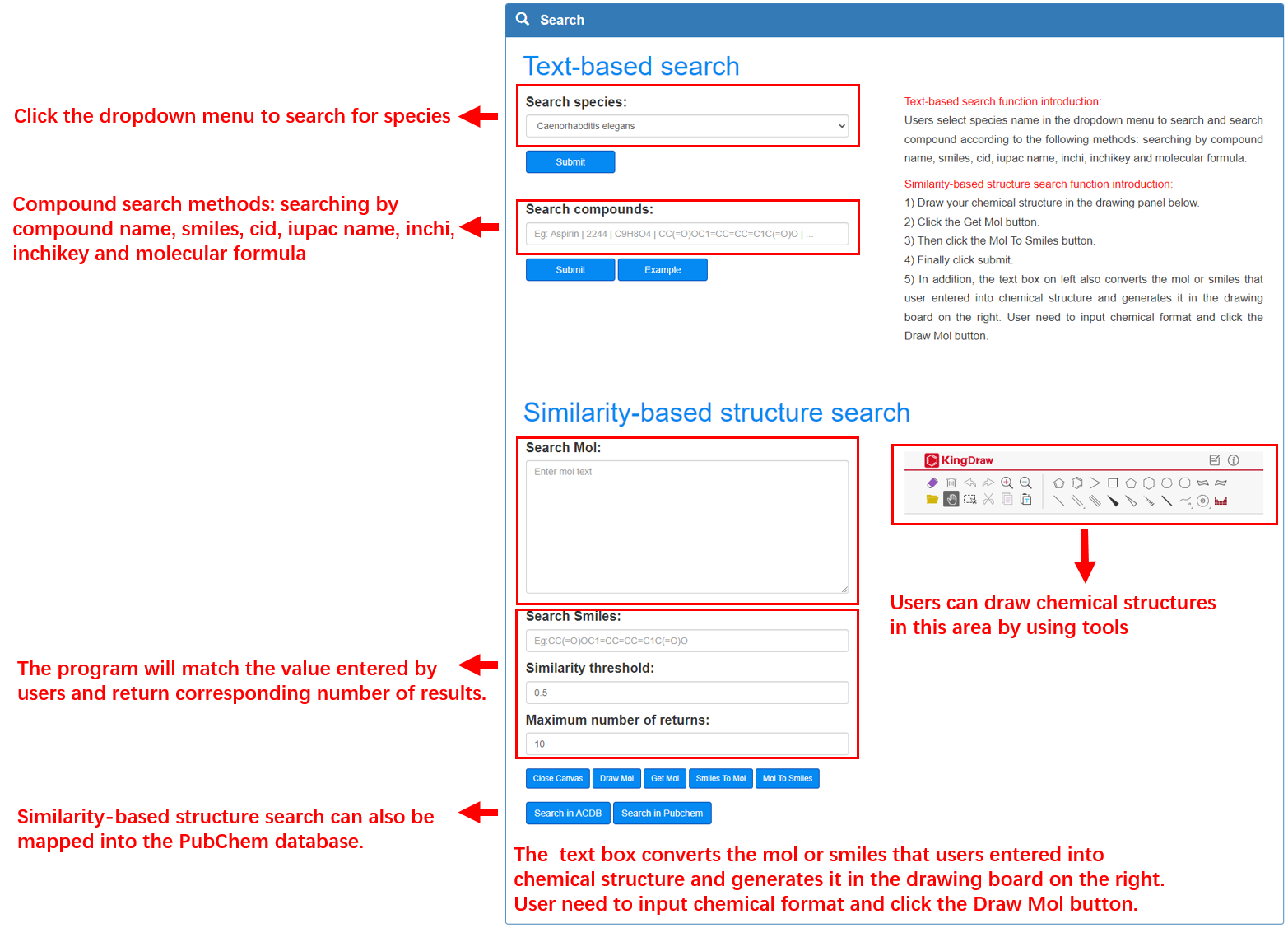
Small molecule information transforms chemical structure:
Mol to structure: Users input a compound with Mol format in the textarea of Search Mol and click the button of Draw Mol to get chemical structure in drawing board on right. Smiles to structure: Users input a compound with Smiles format in the text box of Search Smiles and convert to Mol format by clicking Smiles to Mol button. Then click the button of Draw Mol to get chemical structure in drawing board on right.
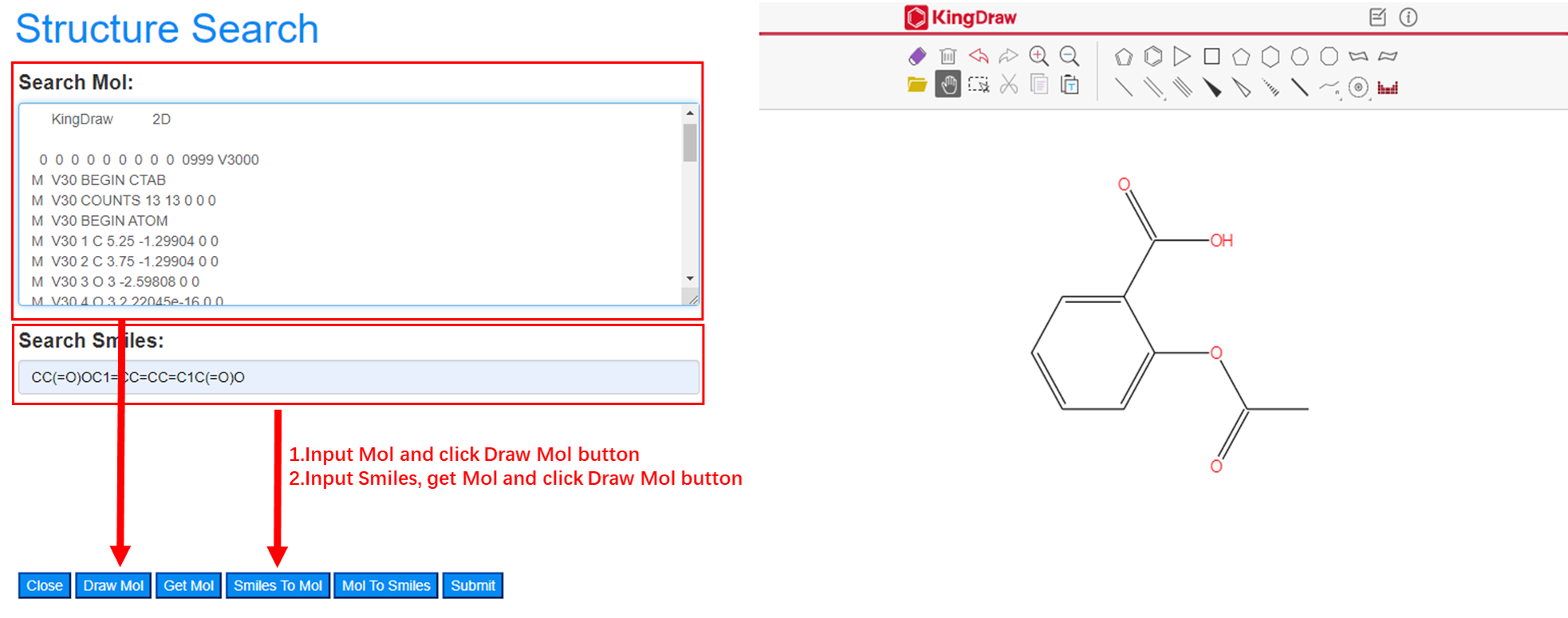
Chemical structure transforms small molecule information:
Users draw a chemical structure on drawing board and get the Mol format by clicking Get Mol button. Smiles format will be given by clicking Mol To Smiles button after get Mol format.

Species search results include three sections:
Experimental Data Experimental Data Visualization Statistics Data Statistics Data Visualization
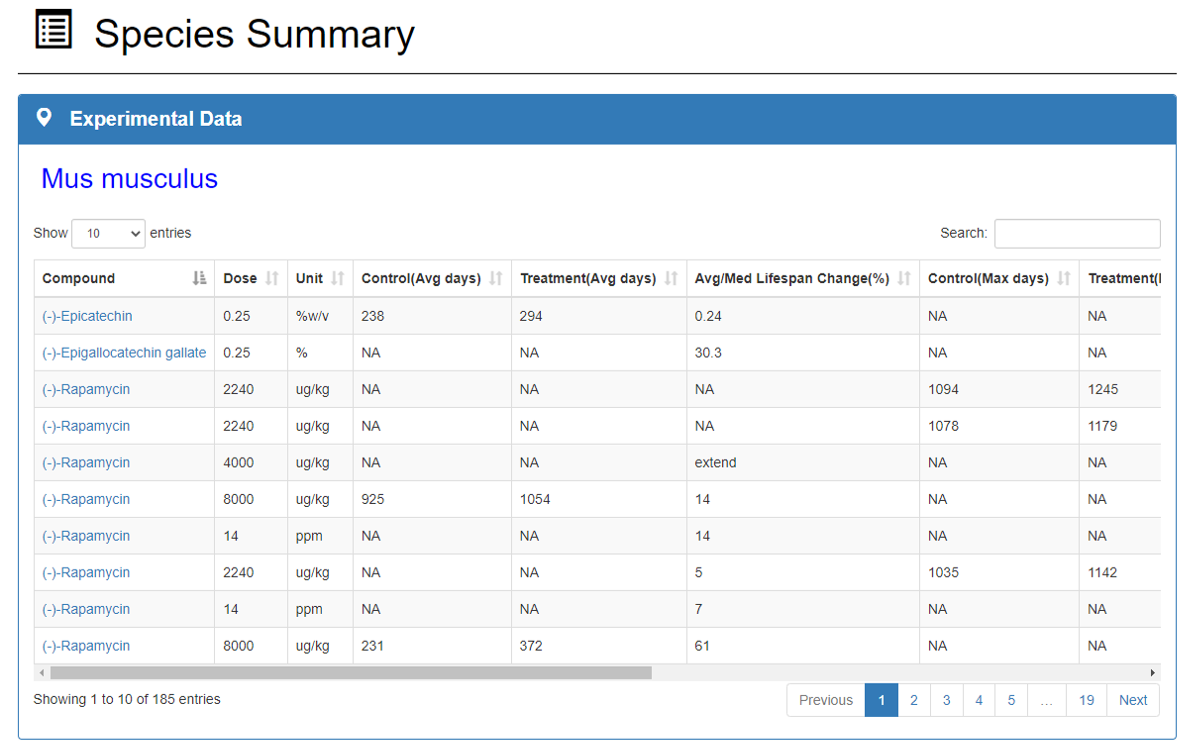
Experimental Data:
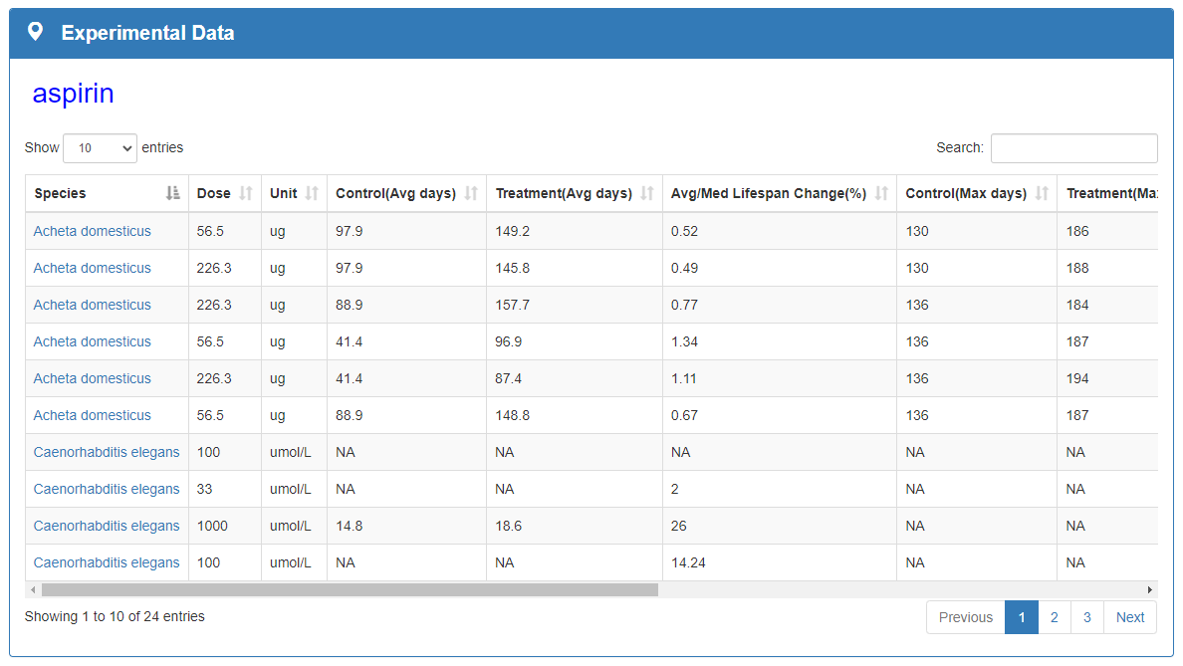
Experimental data section shows the experimental information of the species including compounds and crude extracts, drug dose and concentration, species and strain, mean and maximum survival time, statistical significance and original data sources.
Experimental Data Visualization:
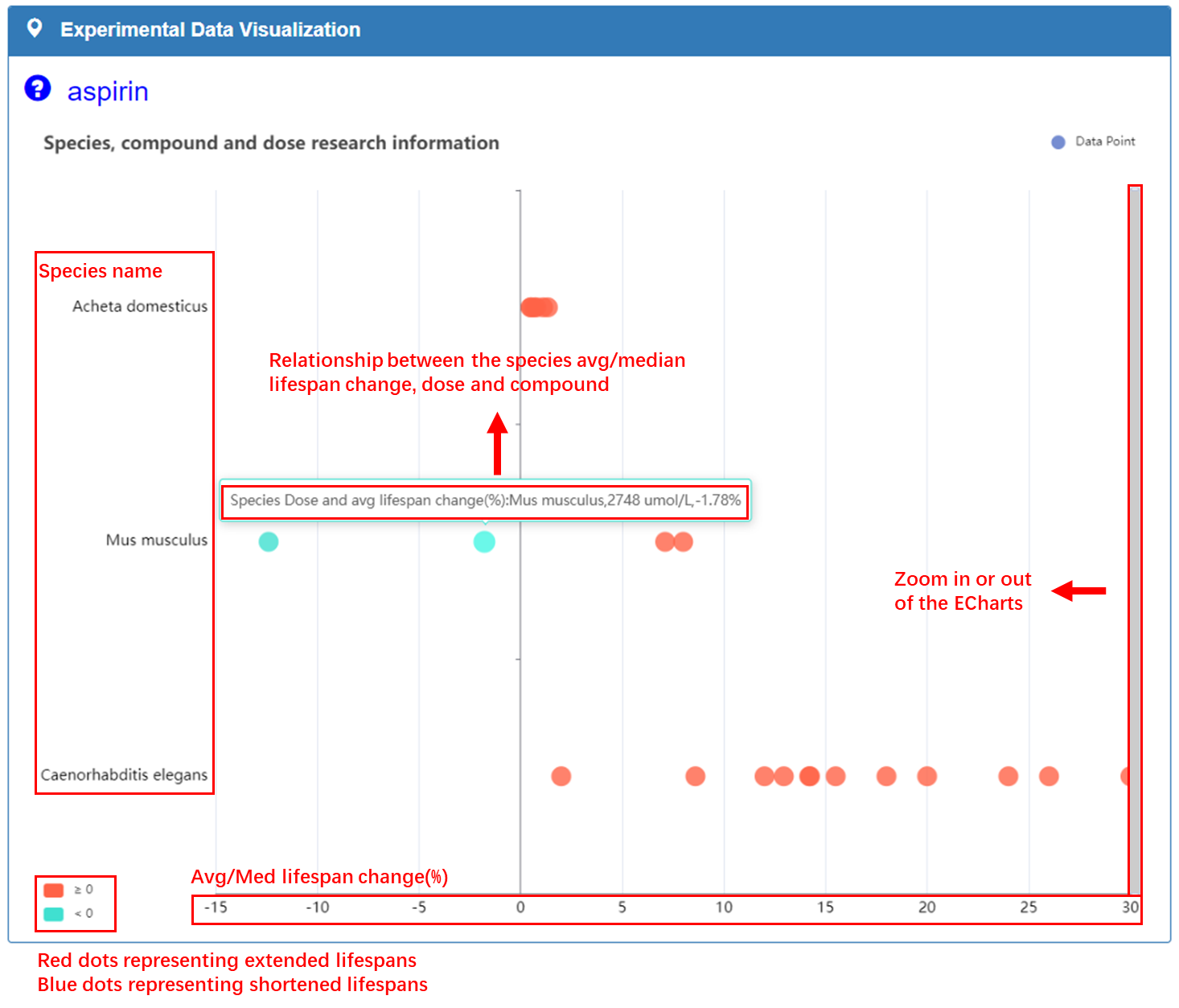
Abscissa represents the effect of compound on the lifespan of the species, with blue dots representing shortened lifespans and red dots representing extended lifespans. Ordinate represents the names of compounds that have been tested in the antiaging field for this species. The dots in graph illustrate relationship between compounds, doses, and species average/median lifespan changes.
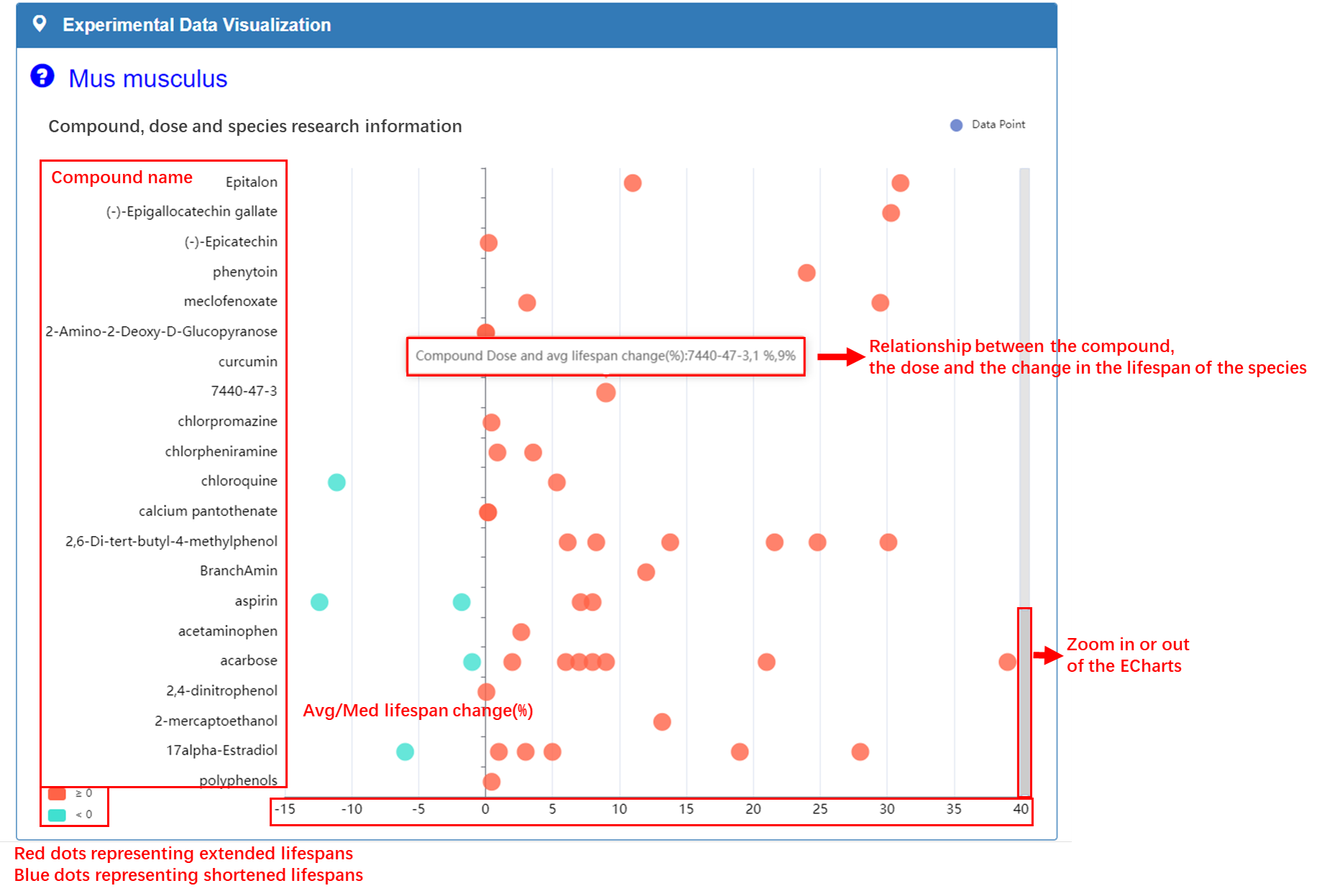
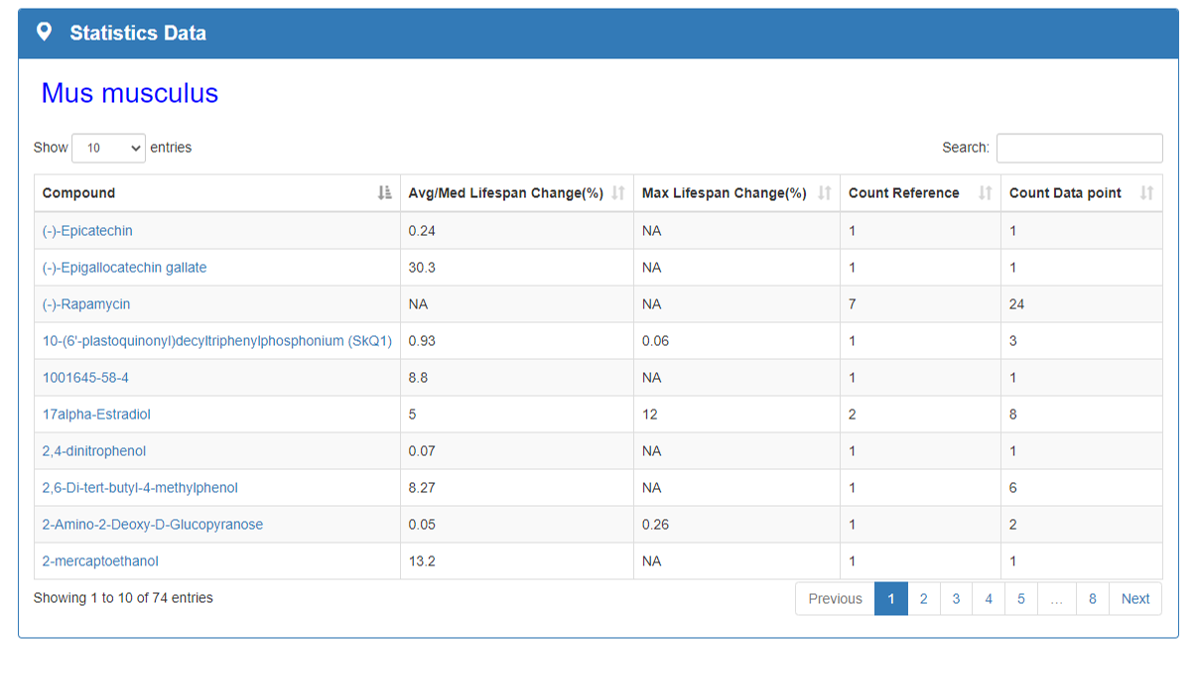
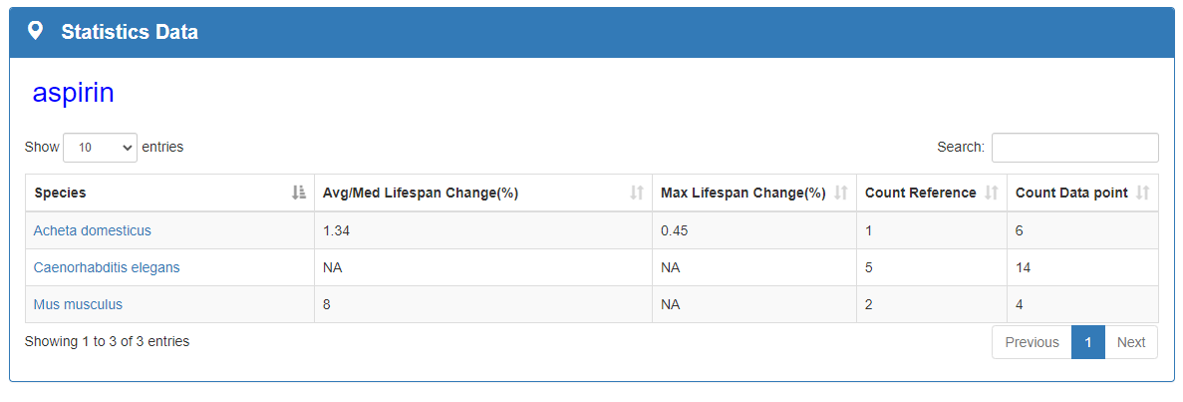
Statistics Data:
This section counts the maximum impact of each compound on the species average/median lifespan and the frequency of each compound studied in articles. Statistics Data part will give clear messages to researchers understand the current research status of aging field.
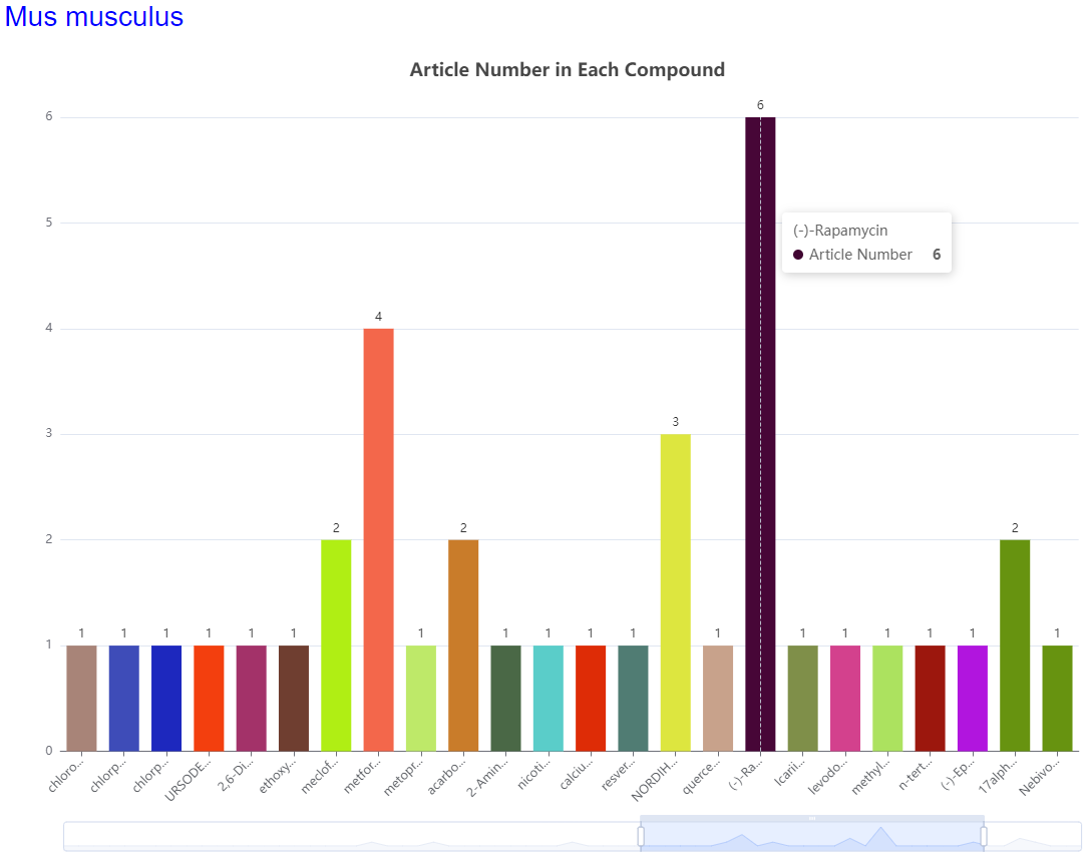
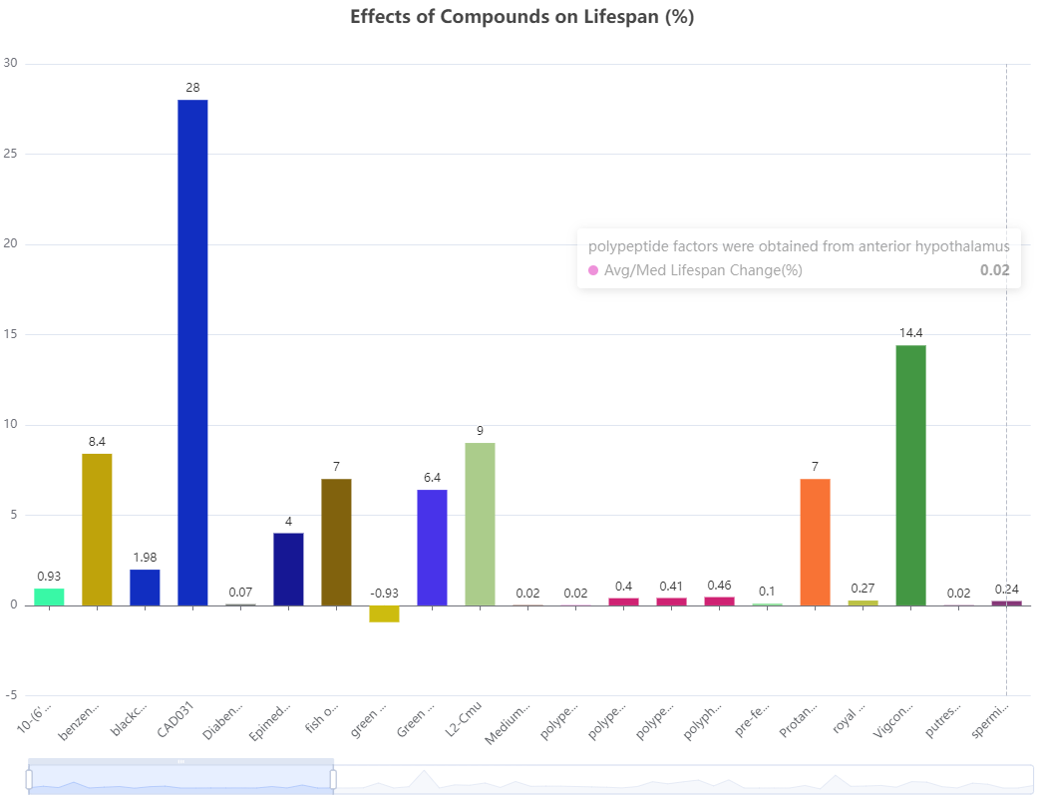
Statistics Data Visualization:
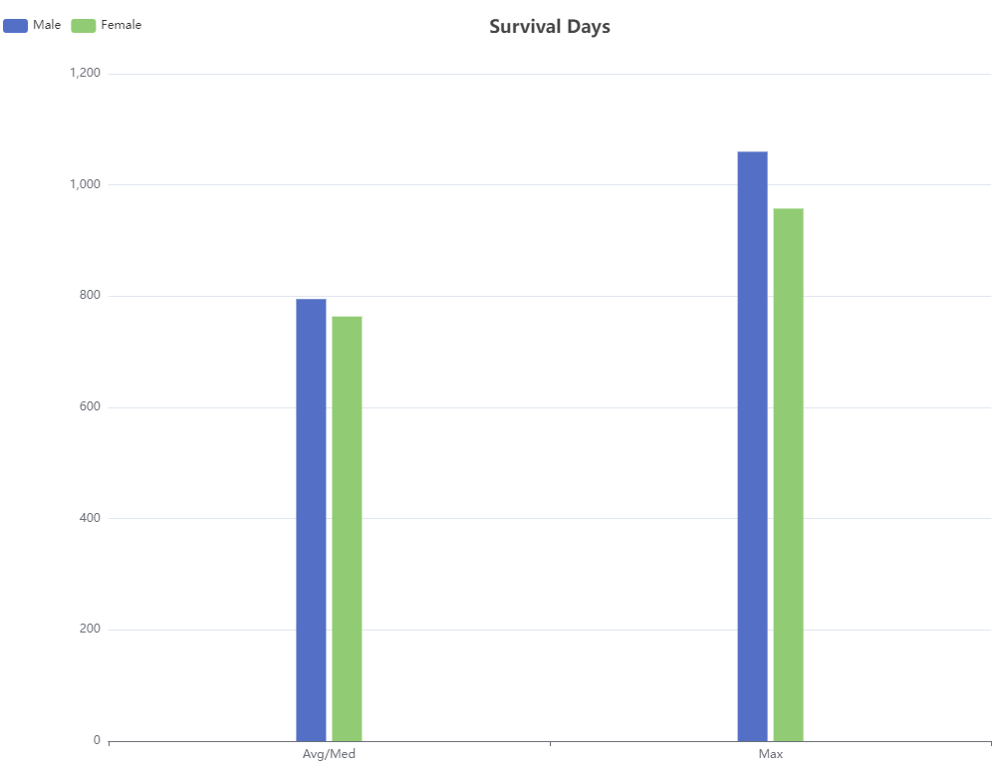
Visualize statistics data and show the average survival time and maximum survival time after medication of species.
Result of text-based search:
Text-based compound search makes fuzzy queries based on users input. Compound name that best matches the users input will be ranked first. Results are presented as compound cards containing chemical information for query compound. Users view details by clicking on compound name.

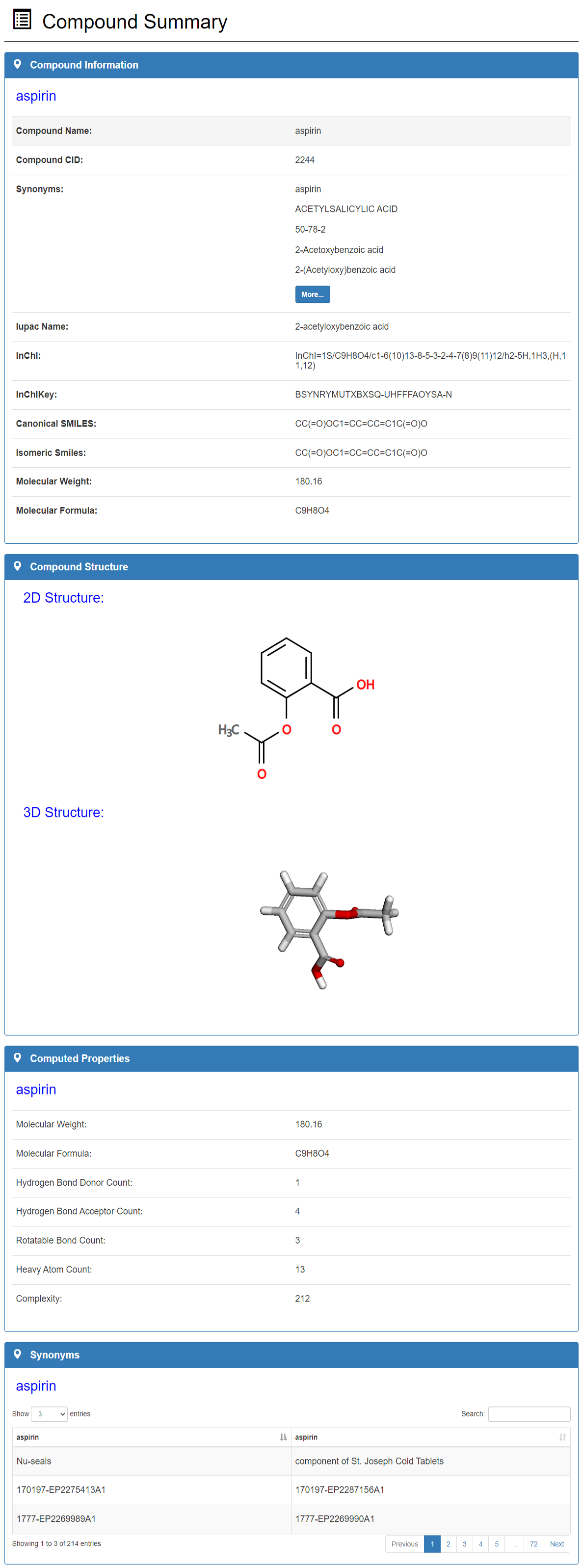
Compound detail page include seven sections:
Compound Information Compound Structure Computed Properties Synonyms Experimental Data Experimental Data Visualization Statistics Data Statistics Data Visualization
Compound overview:
Compound information section includes compound name, compound CID, synonyms, iupac name, inchi, inchikey, canonical smiles, isomeric smiles, molecular weight and molecular formula. User can view compound 2D and 3D structure in compound structure panel and drag compound 3D structure with mouse. In addition, we calculated the molecular weight, molecular formula, hydrogen bond donor count, hydrogen bond acceptor count, rotatable bond count and complexity of the compound.
Experimental Data and Visualization:
Experimental Data, Experimental Data Visualization and Statistics Data sections show experimental information of compound and visualize it. This section counts the maximum impact of each species exposed the compound average/median lifespan and the frequency of each species studied in articles. Statistics Data part will give clear messages to researchers understand the current research status of aging field.
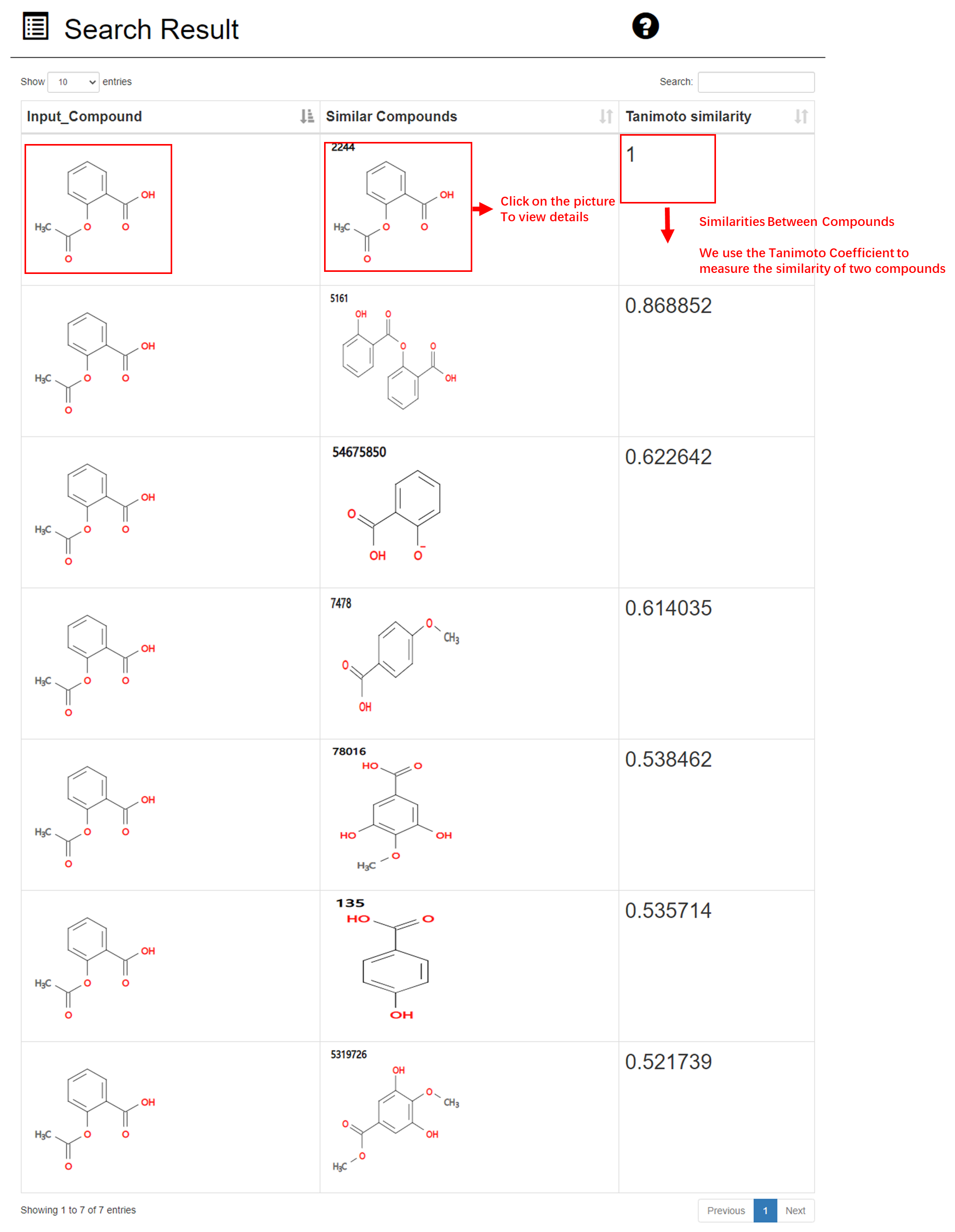
Result of similarity-based structure search:
The results of similarity-based compound structure search are displayed in descending by order of similarity. First column in the table is the compound structure entered by the users. Second column is compound matched in ACDB. We use the Tanimoto Coefficient to measure the similarity between compounds. The larger Tanimoto Coefficient, the more similar two compounds are. In addition, users can view the detailed information of the matched compound by clicking on picture in the second column.
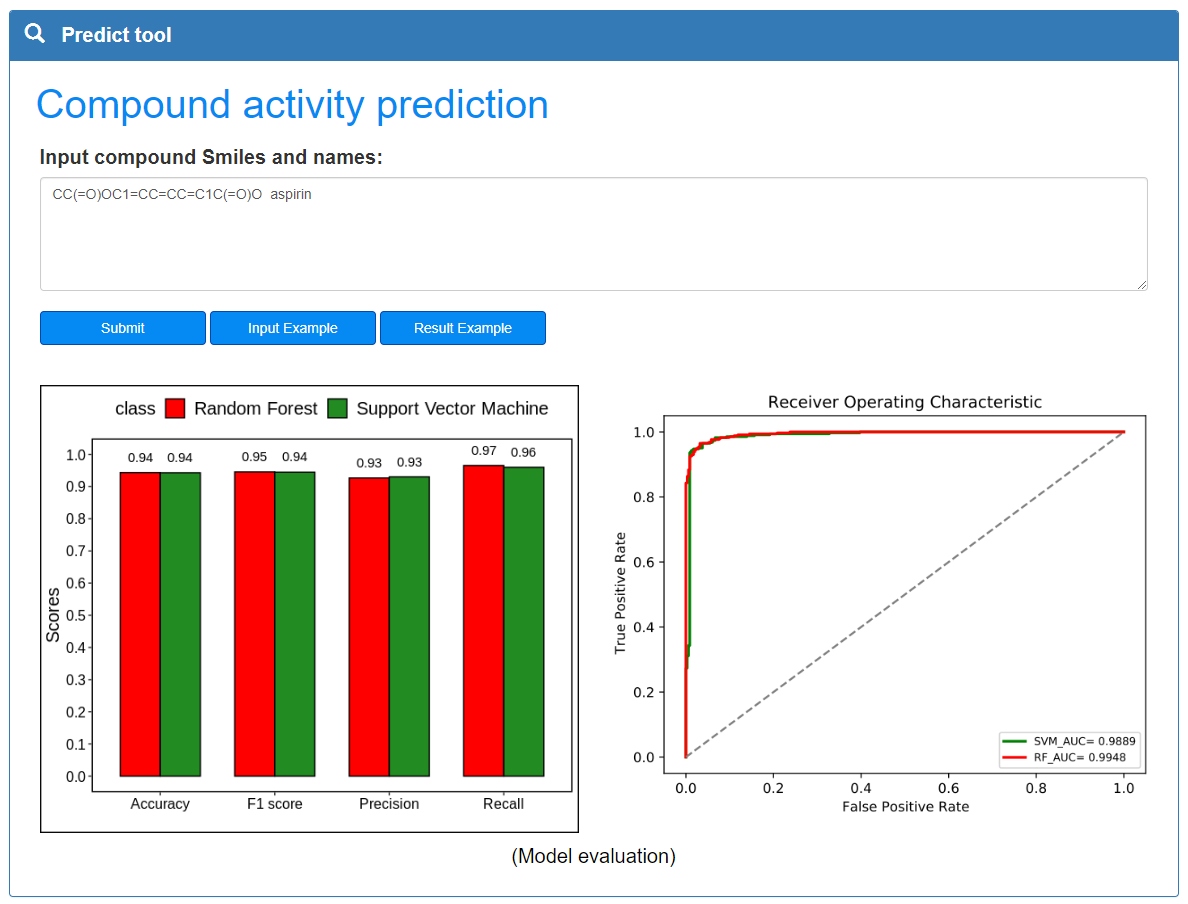
Data predict:
The data predict page provides the compound activity prediction function. User quickly get the activity prediction result of the compound of interest by entering the compound information in the text field below and clicking the submit button. In the result page, user obtains similar compound details by clicking on the picture of the similar compound. In order to ensure the stable operation of the program, please separate the compound Smiles and the name with a tab separator or a space. Example button prompts the user for input.
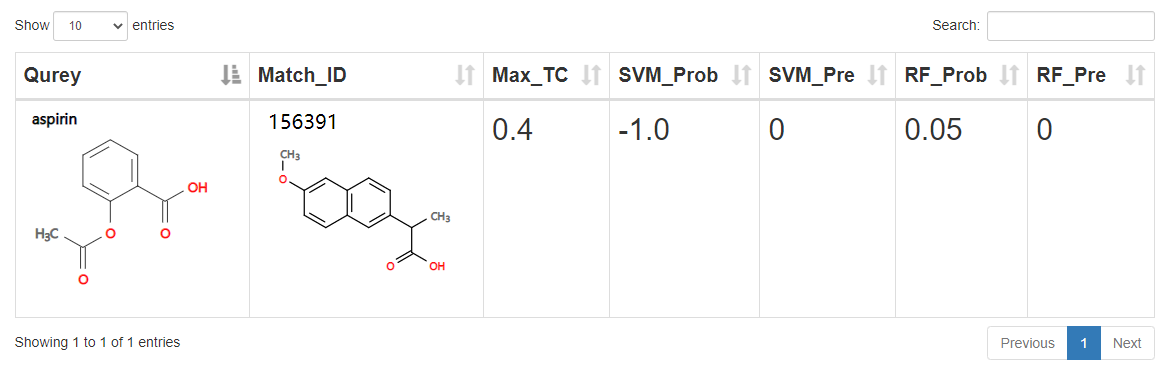
Predict result:
1.Query: 2D structure of the compound queried by the user. 2.Match_ID: ost similar compound matched in ACDB by the query compound. Click on picture to view compound details. 3.Max_TC: Maximum Tanimoto coefficient. Similarity between query compound and match compound. Reflect the novelty of the query compound. 4.SVM_Prob: Prediction Score of Support Vector Machines. Positive score indicates activity and negative score indicates inactivity. 5.SVM_Pre: Support Vector Machines label is 1 to indicate activity and 0 to indicate inactivity. 6.RF_Prob: Prediction score of Random Forest. Score greater than 0.5 indicates activity and less than 0.5 indicates inactivity. 7.RF_Pre: Random Forest label is 1 to indicate activity and 0 to indicate inactivity. 8.Active compounds: drug dose <= 10 & drug units = "umol/L" & average/median lifespan change > 0 & significance = "S" (Mus musculus data sets independent of dose conditions) 9.Inactive compounds: drug dose >= 10 & drug units = "umol/L" & significance = "NS"
Data submit:
Users fill in information in the text box and click submit button and we will add it to ACDB soon. We hope that users can give priority to completing the "necessary information" section and attach an email address for contact.
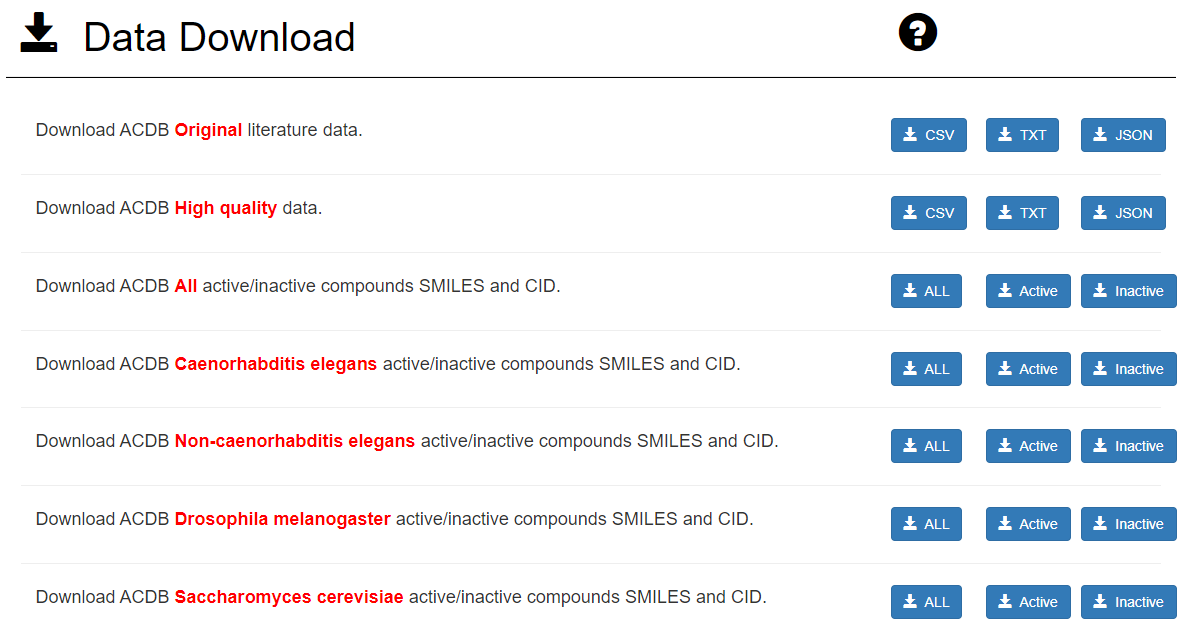
Data download:
Users choose to download corresponding files and formats according to their own research needs. For example, if the users want to explore the raw data, users download the Original literature data. If users want to build a prediction model of Caenorhabditis elegans anti-aging compounds , users download Caenorhabditis elegans SMILES and CID file and download the SMILES and CID files of other species as validation data to check the accuracy of the model. In addition, JSON format is more suitable for database AJAX calls. Original literature data : Raw data and no modification High quality data : Converted drug units, filtered species strains (keep wild type) and removed some bad data points based on raw data All active/inactive compounds : Active compounds : drug dose <= 10 & drug units = "umol/L" & average/median lifespan change > 0 & significance = "S" Inactive compounds : drug dose >= 10 & drug units = "umol/L" & significance = "NS" We recommend users build and tune models by using the largest dataset of Caenorhabditis elegans, and then test model performance by using Drosophila melanogaster, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Non-caenorhabditis elegans datasets. All active/inactive compounds file is used in the final model which is trained close to perfect.